Account 09 in accounting is used when there are discrepancies between the accounting data. and tax accounting. It reflects temporary differences in the amount of deferred tax asset (ITA) in cases where the expenses for calculating income tax are less than the expenses for the same period in accounting, regulated by PBU 18/02. Briefly about the procedure for recording transactions on this account - in the article.
So, if there are more expenses in accounting than in tax, then the income tax in accounting will be less. It is as a result of the accrual of IT on the account. 09 we have to equalize the tax in both accounts. Account 09 shows information about the generated deferred asset and its change in order to equalize the accrued tax between two accounts:
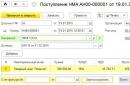
- on debit 09, we reflect the SHA formed in the reporting period in the amount of 20% (tax rate in the reporting period) of the resulting deductible difference. Credited in this case. 68 "Calculations for income tax": Dt 09 Kt 68;
- for loan 09 we show how much SHA decreased in the reporting period, and for a loan we show the full repayment of SHA in certain cases. sch. 68 in this case will be debited: Dt 68 Kt 09.
It is important to organize account analytics in terms of assets and (or) liabilities for which a temporary difference is formed.
For small businesses
Since the formation of differences is not welcomed by accountants, we immediately recall that small enterprises (not subject to mandatory audit) can refuse to use PBU 18/02, do not generate account 09 and use it in accounting and reporting, NPOs are those who have the right to simplified accounting and simplified reporting. This right should be recorded in the accounting policy of such organizations.
How to close account 09 if the organization has the right and decided to refuse the formation of differences? To do this, on 31.12 of the year preceding the year from the beginning of which it was decided not to apply RAS 18/02, we make postings to the balance of the account in accounting. 09:
Dt 84 Ct 09.
In the explanatory note to the reporting for 2017, it is advisable to reflect the fact of refusal to apply RAS 18/02 from the year following the reporting year.
Postings on account 09 for those who are obliged to form accounting differences
Write-off of account 09 upon liquidation of an LLC, as in the case of disposal of the asset for which it was accrued, is reflected:
Dt 99 Ct 09.
If there was a loss on income tax, for example, accounting and tax at the end of 2017 amounted to 2,000,000 rubles. In accounting, we recognize it at a time, and for income tax - in parts in the order Art. 283 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, there is a temporary difference in the amount of 2,000,000 rubles. and from her account. 09 in the amount of 400,000 rubles. (2,000,000 × 20%). We reflect the accrued IT in the accounting:
Dt 09 Kt 68 in the amount of 400,000 rubles.
When using the loss to reduce income tax, you need to show the change in the account. 09. For example, in 1 square. In 2019, the taxable base for income tax amounted to 2,400,000 rubles. In accordance with Art. 283 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the base can be reduced by no more than 50%, that is, by 1,200,000 rubles.
20% from 1,200,000 rubles. is 240,000 - it is for this amount that we have the right to show the change in the account. 09 in the part of SHE for tax loss with the following entry:
Dt 68 Kt 09 in the amount of 240,000 rubles.
When does account 09 close? The remaining SHE for 160,000 rubles. will be debited to 68 until the full use of the remaining loss (1,200,000 rubles) to reduce income tax.
When selling fixed assets with a loss in accounting, the residual value of fixed assets is fully written off as expenses at a time, forming a loss from the sale of fixed assets. In order to Tax Code of the Russian Federation such loss is recognized on a straight-line basis over the remaining life of the asset. There is a temporary difference in the amount of the loss from the sale, IT is formed:
Dt 09 Kt 68 in the amount of 20% of the loss from the sale of fixed assets.
In the months following the month of sale, for the purposes of applying the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, we may recognize a loss from the sale of fixed assets, as a result of which it will decrease. The amount of such a decrease is calculated as the quotient of the division of IT by the loss from the sale of fixed assets and the remaining life of the fixed asset. For the amount of such repayment, a posting is made:
Dt 68 Kt 09 - for the entire remaining life of the implemented OS.
Accounting generates permanent and temporary differences. It depends on this whether the tax asset will be permanent or deferred.
The constant difference includes those amounts that participate in the formation of the balance sheet, but do not affect the taxable amount. This includes the payment of interest, the amount of which is not taken into account in full when calculating income tax. Also, permanent differences include those expenses or incomes that affect only the formation of the tax base. For example, a fixed asset is acquired, the useful life of which in tax accounting is longer than in accounting.
Based on the foregoing, we can conclude that a permanent tax asset is the amount of tax that reduces income tax payable to the budget in the reporting period in which it is formed.
A temporary difference occurs when the amount of accounting and tax accounting does not match, the recognition of expenses shifts over time. That is, in accounting, the amount is recognized in the reporting period in which the operation was performed, and in tax accounting, part of the amount is transferred to the next period.
It is due to the temporary difference that a deferred tax asset is formed, that is, the reducing part of the tax is transferred to the next reporting period. To calculate the amount of the deferred tax asset, you need to multiply the temporary difference by the tax rate. As a rule, deferred tax is reflected in account 09.
The amount of the deferred tax asset is reflected in the income statement (Form No. 2). To obtain this information, open account 09 and calculate the difference between debit and credit.
In the course of the economic activity of the organization, namely, when keeping records, the following situation may arise: when recognizing income or expenses, the accounting amounts differ from the tax. This can occur when applying different depreciation methods. There is a so-called deferred tax asset (DTA), which is formed due to deductible temporary differences. The accountant must write off this SHE when the object is disposed of.
Instruction
To get information about the movement and availability of a deferred tax asset, open account card 09, this is where all the information is located. When creating a deductible temporary difference, multiply it by the income tax rate. The difference may result in the case of depreciation, with an overpaid amount of tax, with the recognition of commercial expenses in the cost of goods sold, and in other cases.
For example, an organization purchased a computer for 35,400 rubles, including VAT 5,400. After some time, it was decided to sell office equipment for 236,000 rubles, including VAT 3,600 rubles. The amount of depreciation in accounting was 8,000 rubles, and in tax accounting - 7,020 rubles. The deductible temporary difference is RUB 980 and the deferred tax asset is RUB 980*24%/100=235 RUB.
In accounting, reflect this as follows: D62 K91 sub-account "Other income" - 23,600 rubles - reflected the proceeds from the sale of a computer; D91 sub-account "Other expenses" K68 - 3,600 rubles - the amount of VAT was charged; 00 rubles - the amount of depreciation was written off according to accounting data; D91 subaccount "Other expenses" K01 - the residual value of fixed assets is written off; D99 K09 - 235 rubles - the amount of the deferred tax liability is paid off; D68 K99 - 235 rubles - the amount of the permanent tax liability is reflected.
Designed to account for deferred tax assets.
The balance of debit 09 of the account means that part of the deferred asset has not been repaid.
If, at the end of the tax period, a loss is reflected in the tax accounting, then additionally you need to make a posting:
– reflects a deferred tax asset from a loss that will be repaid in the next reporting (tax) periods.
This balance will be closed in the following tax periods when the amount of loss is written off at the expense of tax profit.
Oleg Khoroshiy, Head of the Department of Profit Taxation of Organizations of the Department of Tax and Customs Tariff Policy of the Ministry of Finance of Russia
How to reflect the accrual and payment of income tax in accounting
To account for deferred tax assets, use account 09, * and for liabilities - account 77. In subsequent periods, as income and expenses converge in accounting and tax accounting, pay off deferred tax liabilities and assets.
Here is how to record the origination and settlement of deferred tax assets and liabilities:*
| Cause of temporary differences | Type of tax assets and liabilities | How does income tax affect accounting | Postings* |
| Income that is not reflected in the accounting of the current reporting period | Deferred tax assets (DTA) | Reduce the amount of tax for future reporting periods. The tax of the current period is increased |
Debit 09 Credit 68 sub-account "Calculations for income tax" Debit 68 subaccount "Calculations for income tax" Credit 09 |
| Expenses that are not recognized for taxation in the current reporting period | |||
| Income that is not taxed in the current reporting period | Deferred Tax Liabilities (DTL) | Increase the amount of tax for future reporting periods. The current period tax is reduced |
Debit 68 subaccount "Calculations for income tax" Credit 77 Debit 77 Credit 68 sub-account "Calculations for income tax" |
| Expenses that are not reflected in the accounting of the current reporting period |
The size of IT and IT is determined by the formula:
This procedure is provided for in paragraphs 8–12, and PBU 18/02.
About account 09 "Deferred tax assets" and temporary differences
To reflect the differences between the accounts in the Chart of Accounts, special accounts are provided. One of them is account 09 “Deferred tax assets”.* This article will be discussed in the article.
As always, read the problem below first. Take a look at the Chart of Accounts, PBU 18/02 and the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Make your own accounting entries. And only after that, read the explanations in the article and check the solution - it is given at the end of the article.
Why there are differences between accounting and tax accounting
Not only participants or shareholders have the right to claim a part of the company's profit, but also the state. His right to a share in the business is enshrined in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. How? It's very simple: at the expense of profits, organizations are required to pay some taxes. For example, for those who apply the general system of taxation, this is income tax.*
How do you take into account the difference in accounting when selling a fixed asset *
The company LLC "Invest" in June of this year sold the fixed asset. The loss from this operation amounted to 120,000 rubles. The remaining life of the facility is 12 months. In accounting, the loss from the sale of a fixed asset is taken into account in expenses at a time - according to the rules established in paragraph 11 of PBU 10/99. And when calculating income tax, it is written off gradually according to the rules that are given in paragraph 3 of Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Because of this, there is a difference between accounting and tax accounting. What postings to reflect it in June and July of the current year? Suppose that in the accounting of Invest LLC, the reporting period is equal to a month. The company also calculates income tax on a monthly basis.
Only certain categories of enterprises are entitled to reflect it in accounting in the same amount that was calculated according to tax rules. Particularly the small ones. But for the rest there are special rules. They stipulate that the difference between the two indicators should be visible from accounting. The first is profit, which was calculated according to accounting rules. And the second is the profit that the company determined according to the rules of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
How can the same enterprise have two profits? We have already said that the state is, in fact, the second owner of profit. But when dividing the profits, the two owners may have disagreements.
In our example, Invest LLC sold a fixed asset. In accounting, the loss from its sale is attributed to the expenses of the current period. That is, they are included in other expenses at a time - in the month when the sale took place (clause 11 of PBU 10/99). But when calculating income tax, such a loss is written off gradually - during the period that remains until the end of the useful life of the object (clause 3 of article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). * That is, in tax accounting, the Invest company must include 10,000 rubles in expenses every month. (120,000 rubles: 12 months).
Thus, the state, as it were, says: “You acquired a fixed asset not for resale, but for use. So, they planned to amortize it. Now, do not speed up the process by writing off the loss at a time. Let's agree like this. In accounting, you will reflect the real profit of the enterprise. And pay tax on profits calculated in accordance with the rules of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Then, from the point of view of the state interests, everything will be fair.”
What is deductible temporary difference and deferred tax asset
There are two types of differences between accounts: permanent and temporary. A permanent difference occurs when some income or expense is reflected only in accounting or only in tax accounting (in whole or in part). A temporary difference is when income or expense is reflected both in accounting and in tax accounting. But in accounting in one period, and in tax accounting - in another. *
In our example, LLC Invest has a temporary difference. After all, the company will fully include the loss from the sale of fixed assets in expenses not only in accounting, but also in tax accounting. It just happens later in tax accounting.
In our example, in the period when the loss occurred in accounting, it was not fully taken into account when calculating income tax. Instead, its accounting for tax expenses was postponed to the future. As a result, accounting profit turned out to be less than tax profit. The deviation between them, which must be reflected in accounting, is called a deductible temporary difference. And the product of this difference by the income tax rate effective in the reporting period is a deferred tax asset. Thus, it can be calculated by the formula: *
The deferred tax asset is reflected in the credit of account 68 "Calculations on taxes and fees". That is, on the same account that you want to use to account for the accrued and paid amounts of income tax, as well as advance payments on it. Usually, a separate sub-account is opened for this called “Calculations for income tax”.
In our case, special account 09 “Deferred tax assets” corresponds to this account. Thus, the entry that the accountant of Invest LLC must make in June looks like this: *
When and how the deferred tax asset is settled
The company "Invest" sold the fixed asset in June of this year. In the same month, depreciation was charged for the last time in tax accounting for this object. And next month - July - the accountant can write off the first part of the loss - 10,000 rubles - for tax expenses.
As soon as the accountant does this, the temporary difference will be 10,000 rubles. less. And it will no longer be 120,000 rubles, but 110,000 rubles. (120,000 - 10,000). Accordingly, the size of the deferred tax asset should also be adjusted downward. Wiring like this:*
The accountant of Invest LLC will make such postings on a monthly basis until the loss from the sale of fixed assets is fully included in tax expenses. In the period in which this occurs, the temporary difference will vanish, and with it the deferred tax asset.*
Sergey Razgulin, Acting State Councilor of the Russian Federation, 3rd class
How to close reporting periods in accounting and determine financial results during the year. The organization applies the general system of taxation
Conditional income (expense) on income tax
If the organization applies PBU 18/02, then simultaneously with the closing of the reporting period, it is necessary to reflect in accounting the conditional expense (income) for income tax.
To calculate this indicator, use the formula:*
The amount of conditional expense (income) for income tax is reflected in accounting on the sub-account of the same name, which is opened to account 99 “Profit and Loss”.
This procedure follows from the provisions of paragraph 20 of PBU 18/02.
In accounting, reflect the amount of conditional expense (income) by posting: *
– accrued the amount of conditional expense for the reporting period;
Debit 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” Credit 99 subaccount “Conditional income for income tax”
- accrued the amount of conditional income for the reporting period.
If, at the end of the reporting (tax) period, a loss is reflected in the tax accounting, then an additional entry must be made: *
Debit 09 Credit 68 sub-account "Calculations for income tax"
– reflects a deferred tax asset from a loss that will be repaid in the next reporting (tax) periods.
The amount of income tax reflected in accounting at the end of the reporting quarter or year must match the amount reflected in the tax declarationapproved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 26, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/600. Therefore, after making such postings, check whether the reporting period is closed correctly. To do this, compare the total (from the beginning of the year) turnover on account 68 sub-account "Calculations for income tax" in correspondence with the accounts: *
– 09 “Deferred tax assets”;
– 77 “Deferred tax liabilities”;
- 99 "Profit and loss" sub-account "Contingent expense (income) for income tax";
- 99 "Profit and loss" sub-account "Permanent tax liabilities (assets)".
If the difference between the debit and credit turnovers on these accounts coincides with the amount reflected in line 180 of sheet 02 of the income tax declaration, then the income tax calculations are reflected in accounting correctly. This means that the reporting period is closed correctly.*
Depending on the frequency with which the organization reports on income tax, it must do such a check either at the end of each month or at the end of each quarter.
An example of the reflection in accounting of a conditional income tax expense at the end of the reporting period
Alfa LLC calculates income tax on a monthly basis from actual profit. Income and expenses in tax accounting are determined on a cash basis. The organization is engaged in the provision of information services and enjoys exemption from VAT.
In January, Alfa sold services in the amount of 1,000,000 rubles.
The staff of the organization was paid a salary in the amount of 600,000 rubles. The amount of contributions for compulsory pension (social, medical) insurance and insurance against accidents and occupational diseases from the accrued salary amounted to 181,200 rubles.
As of January 31, sales proceeds have not been paid, staff salaries have not been paid, and mandatory insurance contributions have not been transferred to the budget.
On January 15, Alfa manager A.S. Kondratiev submitted an advance report on entertainment expenses in the amount of 24,600 rubles. On the same day, these expenses were reimbursed to him in full. When calculating income tax, hospitality expenses in the amount of 24,000 rubles were taken into account. (600,000 rubles x 4%).
In January, Alfa had no other operations. The following entries were made in the accounting records of the organization:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
- 1,000,000 rubles. - reflects the proceeds from the sale of information services;
Debit 68 subaccount "Calculations for income tax" Credit 77
- 200,000 rubles. (1,000,000 rubles x 20%) - reflects a deferred tax liability from the difference between the revenue reflected in accounting and tax accounting;
Debit 26 Credit 70
- 600,000 rubles. - salary for January;
Debit 09 Credit 68 sub-account "Calculations for income tax"
- 120,000 rubles. (600,000 rubles x 20%) - a deferred tax asset is reflected from the difference between the salary reflected in accounting and tax accounting;
Debit 26 Credit 69
- 181,200 rubles. – mandatory insurance premiums were accrued from the salary for January;
Debit 09 Credit 68 sub-account "Calculations for income tax"
- 36,240 rubles. (181,200 rubles x 20%) - a deferred tax asset is reflected from the difference between the amount of taxes (contributions) reflected in accounting and tax accounting;
Debit 26 Credit 71
- 24,600 rubles. - representation expenses are written off;
Debit 99 subaccount "Permanent tax liabilities" Credit 68 subaccount "Calculations for income tax"
- 120 rubles. ((24,600 rubles - 24,000 rubles) x 20%) - a permanent tax liability is reflected from the amount of representation expenses reflected in accounting and tax accounting;
Debit 90-2 Credit 26
- 805 800 rubles. (600,000 rubles + 181,200 rubles + 24,600 rubles) - the cost of services sold has been written off;
Debit 90-9 Credit 99 sub-account "Profit (loss) before tax"
- 194,200 rubles. (1,000,000 rubles - 805,800 rubles) - profit for January is reflected;
Debit 99 subaccount "Conditional income tax expense" Credit 68 subaccount "Calculations for income tax"
- 38,840 rubles. (194,200 rubles x 20%) - the amount of contingent income tax expense has been accrued.
In January, Alpha's tax records showed a loss of 24,000 rubles. (paid entertainment expenses). Since this loss will affect the determination of the tax base in the following periods, an entry is made in accounting:
Debit 09 Credit 68 sub-account "Calculations for income tax"
- 4800 rubles. (24,000 rubles x 20%) - reflects a deferred tax asset from a loss not recognized in the current reporting period.
The amount of income tax reflected in the declaration for January is zero. The balance on account 68 subaccount "Calculations for income tax" is equal to:
200 000 rub. - 120,000 rubles. - 36,240 rubles. - 120 rubles. - 38,840 rubles. - 4800 rubles. = 0.
The contingent income tax expense is correctly reflected. The reporting period is closed correctly.
Account 09 of accounting is an active account "Deferred tax assets", serves to reflect deferred tax assets (ITA). With the help of practical examples and postings, we will consider how account 09 is used in accounting, and we will also study the features of reflecting transactions for accounting for deferred tax assets.
The change in the value of SHE recognized in accounting is determined as follows: Deductible temporary difference * Income tax rate, Where
SHE are recognized in the reporting period in which the recognized expenses (income) in accounting and tax accounting do not match.
The reason for the non-match may arise due to the use of different methods, for example:
- In the case of using different methods of depreciation of fixed assets;
- Recognized loss on sale of fixed assets. In accounting, the loss is reflected at a time, and in tax accounting, the loss is reflected over a certain period of time;
- Various ways of recognition of business expenses in accounting and tax accounting;
- If the accrual method is used in accounting for expenses, and the cash method is used in tax accounting.
Typical postings on account 09 "Deferred tax assets"
Examples of operations on account 09
Let us consider in more detail examples of operations on account 09 “Deferred tax assets”.
Get 267 1C video lessons for free:
Example 1: Increase in deferred tax assets
Let's say that VESNA in the 1st quarter of 2016 received materials from a supplier in the amount of 590,000 rubles, incl. VAT - 90,000 rubles. and then put them into production. In the 1st quarter of 2016, she transferred 295,000 rubles to the supplier for materials, incl. VAT - 45,000 rubles.
"VESNA" according to the accounting policy, recognizes income and expenses for taxation purposes on a cash basis. The tax rate is 20%. Respectively:
- In accounting, the recognized expense will be equal to - 500,000 rubles. (590,000 - 90,000);
- In tax accounting, the recognized expense is 250,000 rubles. (295,000 - 45,000);
- The deductible difference is 250,000 rubles. (500,000 - 250,000).
"VESNA" in the 2nd quarter of 2016 fully repaid the debt to the supplier. Postings for the accrual and write-off of a deferred tax asset are formed according to the table:
| Dt | ct | Posting amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 10 | 60 | 500 000 | Reflected materials credited to the warehouse | Waybill (TORG-12) |
| 19 | 60 | 90 000 | Accounted for VAT on materials credited to the warehouse | Invoice received |
| 60 | 51 | 295 000 | The transferred part of the money to the supplier for materials is reflected | Bank statement |
| 09 | 68.04.2 | 50 000 | According to the results of the 1st quarter, the accountant made a posting: for 50,000 rubles. increased the amount of IT (250,000 * 20%) | |
| 60 | 51 | 295 000 | Reflected repaid debt to the supplier for materials | Bank statement |
| 68.04.2 | 09 | 50 000 | Redeemed SHE | |
| 99 | 09 | 50 000 | Written off the amount of SHE |
Example 2: Deferred tax assets on loss
For example, in January 2017, VESNA sold its fixed asset. The loss from the sale of fixed assets is 180,000 rubles. At the time of implementation, the remaining operating life of the OS was 6 months.
In accounting, the loss is attributed to financial results in January 2017, in tax accounting, the loss is evenly written off as expenses over the remaining life of the fixed asset (paragraph 3 of Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Accordingly, upon the sale of fixed assets, a deductible difference in the amount of 180,000 rubles was formed. and formed SHE.
Starting from February 2017, in the VESNA tax accounting, 6,000 rubles (36,000/6 months) should be included in expenses every month.
Postings to settle a deferred tax asset:
| Dt | ct | Posting amount, rub. | Wiring Description |
| 09 | 68.04.2 | 36 000 | The amount of IT is reflected (180,000 * 20%) |
| 68.04.2 | 09 | 1 200 | Partial redemption of IT in February (6,000 * 20%) |
| 68.04.2 | 09 | 1 200 | Partial repayment of IT in March (6,000 * 20%) |
| 68.04.2 | 09 | 1 200 | Partial repayment of IT in April (6,000 * 20%) |
| 68.04.2 | 09 | 1 200 | Partial repayment of IT in May (6,000 * 20%) |
| 68.04.2 | 09 | 1 200 | Partial repayment of IT in June (6,000 * 20%) |
| 09 | 09 | 30 000 | Difference between revolutions (36,000–6,000) |
It is important to note that the difference between the turnovers is reflected in line 141 f.2 "Profit and Loss Statement" at the end of the year.
In the case when the credit turnover on account 09 exceeds the debit one, then the indicator on page 141 will be negative, and is entered in f.2 in parentheses. When calculating net profit, the accountant takes into account this amount with a minus sign.
PBU 18/02 is one of the most complex, "mysterious" of all existing rules and procedures in accounting. The initial reading of it leads to complete confusion and confusion among accountants. The document is full of complex terms and postings uncharacteristic for current work.
One of the points covered in PBU 18/02 is a deferred tax asset. IT is accounted for invoice 09.
Account 09 in the accounting system is active, collects information on SHE. A debit accumulates amounts, and a credit writes them off.
So, deferred tax asset- these are the total differences in income tax that appear when there are differences in the information of accounting and tax accounting. Deviations according to information in BU and NU are called deductible temporary differences (RTD), that is, they exist only for a certain period.
In simple terms, on the account 09 is formed share of income tax that is carried forward to subsequent periods. That is, the company transfers, temporarily postpones the fulfillment of the obligation to pay tax to the budget.
During the year, account 09 accumulates amounts for each operation separately. Merging is not allowed. At the end of the period, the generated result is subject to transfer to the balance sheet in line 1180 of the non-current assets section(clause 23 PBU).
Due to the difference in the requirements for accounting for expenses and income in accounting and tax accounting, the same business transactions can generate completely different results.
SHE are formed if, at the request of accounting, expenses are accepted at a time at the time of the business transaction, and in NU they are distributed over subsequent periods. Also, the factor in the occurrence of the balance on the debit of account 09 is the situation with the benefit accepted into the tax base in NU, but not formed in BU.
According to the totality of profits and costs of the company in accounting, the amount of NNP is determined, called conditional, and in NU - current. It is the base calculated at NU that is the basis for calculating liabilities payable to the state budget.
Here are some typical situations that affect the formation of SHE:
- The amount of tax transferred to the budget exceeds the amount of the accrual.
- In BU formed a reserve for holiday pay.
- Various methods.
- The procedure for accepting commercial and administrative expenses in accounting and NU.
- Loss on sale of fixed assets.
These situations lead to the fact that the amount of conditional return is lower than the current one. Accordingly, the amount of the tax also turns out to be different in the values for BU and NU. Such differences are a deferred tax asset.
The decision to keep records of SHE is taken by each organization independently and is fixed in the accounting policy.
Formulas for calculation
SHE according to paragraph 21 of PBU 18/02 are determined by the following expression:
Deferred tax asset = Temporary difference * effective NIT rate (for 2018 - 20%)
Assets of the tax type reduce the actual and increase the notional tax in subsequent periods of time.
That is, when the period of recognition of accounting costs in NU or the formation of income in BU comes, there is reverse difference: the conditional tax becomes greater than the current one. At this point, SHE decreases.

If there is a disposal of an object, an operation that led to the formation of an SHE, then the amount from account 09 is debited to the account of financial results - 99.
Typical wiring
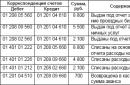
Let's define correspondence of accounts to reflect operations related to the increase and decrease in IT:
| Action | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| emergence | 09 | 68 |
| Closing the fund | 68 | 09 |
| Disposal of the object of occurrence | 99 | 09 |
Examples
Let's prepare an overview of specific situations on the formation of turnovers on account 09.
Increase
PJSC "Maska" in accepting income and expenses for the tasks of calculating tax amounts uses the method of accounting for the final payment.
On February 10, 2017, the company purchased self-tapping screws from Stolb JSC in the amount of 90,000 rubles, incl. VAT – RUB 13,728.81 Inventory and materials transferred for use in the production process.
According to the results of the 1st quarter of 2017, PJSC Maska made only a partial payment for the supplied self-tapping screws, namely, 70,000 rubles, incl. VAT RUB 10,677.97
The tax rate is 20%.
- The BU recorded costs in the amount of 76,271.19 rubles. (90,000 - 13,728.81).
- At NU, the costs amounted to 59,322.03 rubles. (70,000 - 10,677.97).
- We determine the deductible temporary difference - 16,949.16 rubles. (76,271.19 - 59,322.03).
As of April 20, 2017, payment obligations to Stolb JSC were fulfilled in the whole amount.
postings:
| Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. | business transaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 60 | 76271,19 | Self-tapping screws accepted |
| 19 | 60 | 13728,81 | Input VAT |
| 60 | 51 | 70000,00 | Partial payment for goods and materials |
| 09 | 68.04.2 | 3389,83 | The amount of IT has increased (16949.16 * 20%) following the results of the 1st quarter of 2017. |
| 60 | 51 | 20000,00 | Final delivery fee |
| 68.04.2 | 09 | 3389,93 | Closing IT |
| 99 | 09 | 3389,93 | Written off the amount of SHE |
At a loss
On May 20, 2017, Dorma LLC sold a milling machine, which is an OS. The sale brought the company a negative result in the amount of 210,000 rubles. At the time of transfer of ownership, the remaining useful life was 7 months.
In accounting, existing losses will be attributed to the final economic result immediately in May, and in NU they will be distributed proportionally over seven months (Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). As a result, BP is determined in the amount of 210,000 rubles.
From June to December 2017, NU will incur costs in the amount of 6,000 rubles every month. (42,000 / 7 months).
Write-off of the debit balance from account 09 will be reflected following postings:
Amount adjustment
Until January 1, 2017, PJSC Prestige did not include the application of RAS 18/02 into its accounting policy. And as a result of the inventory, it revealed an error in calculating IT in 2016 in the amount of 1000 rubles. It was decided to make an adjustment in order to correct the accounting and achieve the reliability of accounting information. To do this, the specialist draws up an accounting statement with entries: D-84, K-09 for the amount of the discrepancy.
accrual
Based on the results of work in 2016, Mars JSC found that the financial result of the activity for the year was a loss in the amount of 100,000 rubles. In BU, monetary losses will be reflected by the last day of the current year, and NU will be transferred to the next period.
Posting at the end of 2016 will be:
| date | Amount, rub. | Operation | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.12.2016 | 20000,00 | SHE from the amount of loss | 09 | 68 |
emergence
According to the accounting records of the company DSK for 2015, the amount of fixed assets depreciation equal to 1 million rubles was accrued. At NU, these expenses amounted to 800,000 rubles, VVR amounted to 200,000 rubles. The company's revenue is 35 million rubles.
Accountant issued following entries:
| Action | Sum | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Profit | 35000000 | 62 | 90.01 |
| Depreciation costs | 800000 | 20.01 | 02 |
| Costs - VVR | 200000 | 20 (VR) | 02 |
| Cost write-off | 800000 | 90.2 | 20 |
| Closing of VVR | 200000 | 90.2 | 20 (VR) |
| Fin. result | 34200000 | 90.9 | 99 |
| Calculation of NNP (20%) | 684000 | 99 | 68 (NNP calculation) |
| Reflection SHE | 40000 | 09 | 68 |
Write-off
Let's use the conditions of the previous situation and assume that JSC "Mars" in 1 sq. 2017 reached a profitable result with the amount of 1 million rubles. It was decided to reduce the amount of tax due to the loss of the previous year:
| date | Amount, rub. | Operation | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.03.2017 | 20000,00 | Redemption of SHE | 68 | 09 |
Account balance
If at the end of the reporting period there is a balance on account 09, this means that part of SHE did not pass the repayment, for example, if a company has worked for the second reporting period in a row with a loss, there is no tax payable and it is not possible to apply IT. Then the losses are carried forward to subsequent, possibly more successful periods for the company.
How to close
If at the end of the tax period there is a balance on the debit of account 09, and the current amount of tax payable is zero, then closing of the balance can be made only in the next period.
The carrying amount of SHE is reviewed during the preparation of periodic reporting and reduced if there is no possibility of applying a deduction in taxable profit.
A deferred tax asset is an effective tool for applying PBU 18/02 on the way to improving financial policy standards. The calculated deferred net income in accounting and regulated reporting allows completely prevent the occurrence of deviations in the recognition of income and expenses.
This manual provides additional information on this account.