Carrying out their economic activities, some domestic organizations use cash and carry out cash payments. At the same time, domestic legislation allows the use for subjects of civil legal relations or parties to labor relations the circulation of monetary documents, the accounting of which the relevant organization is obliged to carry out in the prescribed manner.
Documents that are monetary
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, by its Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000, approved not only the Chart of Accounts for Accounting for the Financial and Economic Activities of Organizations, but also the Instructions for its Application.
Also, special attention should be paid to the need to produce and issue a cash receipt order, if such documents are handed over to the cash desk of the enterprise. If the documents are issued to third parties from the cash desk of the organization, then the organization needs to issue an expense cash warrant.
A significant difference between CRS and PKO for cash documents from cash documents, the need for which arises when making cash settlements, is the need to put on cash documents to account for documents that are cash, the record "stock".
All received or issued documents must be reflected in the register of cash documents. It should be remembered that such registration is carried out separately from the registration of cash documents for cash settlements.
Accounting for monetary documents
In addition to the need to reflect the movement of documents in the cash book and the register of cash documents, section 5 of the Instruction provides for a general procedure for accounting for documents that are monetary.
By virtue of the named norms of domestic law, analytical accounting is carried out by types of documents on account 50 "Cashier".
For transactions with monetary documents, accounting is carried out in the debit of account 50, if the documents are received by the company's cash desk. If documents are issued from the cash desk of the company, then accounting takes place on the credit of account 50.
In the cash book, it is necessary to register and reflect documents both incoming to the cash desk of the enterprise and issued from the cash desk of the organization to third parties. But such accounting is carried out on separate sheets of the cash book, on which the “stock” mark must be affixed.
As follows from the guidelines for the application and filling out the cash book, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2015 No. 52n, the cash book of the organization reflects the movement of cash documents. For these purposes, separate sheets of the book are used, in which the label "stock" should be affixed.
When filling out the cash book for accounting for monetary documents, it should be remembered that the lines of the book "and" at the cash desk at the end of the day "are not filled.
Entries regarding the movement of documents that are monetary should be made immediately after the issuance or receipt of the corresponding document.
In conclusion, it should be noted that, unlike cash payments, the legislator has not developed or provided for the form of the document used to account for monetary documents issued to third parties.
As provided for in paragraph 1 of Art. 9 of the Federal Law "On Accounting", each fact of the economic activity of the enterprise must be confirmed by the corresponding primary document.
Such documents can be not only approved forms, but also forms independently developed by the relevant business entity. A mandatory requirement for such documents is the presence in them of the details directly listed in paragraph 2 of Art. 9 of the Federal Law "On Accounting".
From the foregoing, it follows that in order to properly record the movement of such documents, an enterprise using them must independently develop a form of a statement of the movement of monetary documents with the obligatory indication of all necessary details in such a statement.
It is important to remember that, regardless of the fact that such documents are not cash, domestic enterprises and organizations are required to keep records of such documents.
Failure by a company to fulfill its statutory obligation to record monetary documents may be grounds for imposing an administrative fine on such a company or its officials for violating cash discipline.
Cash desks of organizations can work not only with cash, but also with monetary documents. Monetary documents are papers purchased for non-cash or cash. They are kept in the cash room safe.
Cash documents include:
- Postage stamps;
- Coupons for fuel (for example, gasoline);
- Tickets for travel on various transport;
- Various vouchers purchased by the organization;
- food stamps;
- Cards for payment of communication services;
- Other Documents.
- Shares purchased from shareholders;
- Various securities;
- Documents for intangible values.
How money is stored
Companies must keep monetary documents in the cash register along with cash. In boo. accounting operations with monetary documents should be reflected in sub-accounts to the account "monetary documents" (50-3).
Accounting for cash documents in accounting. accounting
Consider how some monetary documents are taken into account.
Student Meal Coupons
Some students (pupils, students) educational institutions are required to provide free lunches and breakfasts. This food is issued on special coupons. They should contain:
- Number;
- Validity;
- Meal type (lunch or breakfast);
- Price;
- Seal of the company that issued this coupon;
- The signature of the officer responsible for the issuance.
If educational institutions supply coupons, the manager of this institution must ensure the safety of these coupons. He issues them to the employee who is responsible for organizing free meals. Coupons are transferred under a special act. Coupons that have not been used must be returned to the facility manager. All actions performed with coupons are entered into a special coupon ledger.
If the institution itself provides free meals, at the end of each day the used coupon forms are counted and attached to the cash register. They must be kept for five years after their use.
Stamps
Despite the fact that the technical process is actively developing, postal services remain the same in demand. It is possible to carry out postage only with the help of special stamps. Organizations must account for these stamps as monetary instruments.
Postage stamps are issued to responsible employees as they become needed. Responsible employees must draw up advance reporting, attaching supporting documents to it. The supporting documents are:
- In case of successful sending - sending register;
- In case of unsuccessful sending (damage) - a damaged envelope.
Communication service payment cards
Employees of companies often use corporate communications, and they receive compensation for using their own communications for business purposes. Organizations often pay for communication with special cards. The organization buys them and records them as monetary instruments.
So that the tax authorities do not have unnecessary questions regarding the payment of expenses for communication services, a special provision should be developed in the organization. It should contain a list of employees eligible for special payment cards.
Documents such as gasoline or student meal coupons, postage stamps and envelopes with stamps for sending correspondence, express Internet and cell phone cards, and other documents that require special accounting are often used in the activities of any institution. In the article, we will consider in what order they should be used and taken into account.
What are cash documents
Monetary documents are documents acquired and stored in an institution and have some value. Settlements for their acquisition between the parties have already been made, but the services that can be obtained with the help of these documents have not yet been rendered.According to paragraph 169 of Instruction No.157n paid coupons for gasoline and oil, for food, paid vouchers to rest homes, sanatoriums, camp sites, received notices for postal orders, postage stamps, envelopes with stamps and state duty stamps - all these are monetary documents.
Cash documents must be kept at the cash desk of the institution.
In accordance with paragraph 170 of Instruction No.157n receipt at the cash desk and issuance from the cash desk of such documents are drawn up by incoming cash orders (f. 0310001) and outgoing cash orders (f. 0310002) with the entry "stock" on them.
Incoming and outgoing cash orders with the entry "stock" are registered in the register of incoming and outgoing cash documents separately from incoming and outgoing cash orders, in which operations with cash are recorded.
In the cash book (f. 0504514) of the institution, transactions with monetary documents are recorded on separate sheets, on which the “stock” mark is affixed.
According to the guidelines for maintaining a cash book, approved Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No.173n, totals of operations for the day and indicators of the balance at the end of the day are formed for cash and for monetary documents separately. In the sheets of the cash book containing data on the movement of monetary documents, the lines “including wages” and “total cash balance at the end of the day” are not filled.
Entries in the cash book must be made by the cashier immediately after receiving or issuing monetary documents for each stock receipt and stock expenditure order.
Accounting for transactions with monetary documents is kept in the journal for other transactions on the basis of documents attached to the cashier's reports ( paragraph 172 of Instruction No.157n).
Reflection in accounting of the movement of monetary documents
Let's look at examples of how various types of monetary documents are used in educational institutions and how the facts of economic life performed with their help are reflected in accounting. Specific recommendations for accounting for certain types of monetary documents at the federal legislative level have not been developed, therefore, in our opinion, the procedure for their use and reflection in accounting must be fixed in the accounting policy based on the specifics of the institution.Food coupons for students. There is a category of students to whom the educational institution is obliged to provide free meals. Such food is sold on food stamps. The coupon can be made in a typographical way or printed on a printer. It must contain a number of mandatory details:
Individual number;
Validity;
Type of food;
Amount (cost);
Seal or stamp of the issuing organization and signature of the responsible officer.
For municipal institutions in some regions, rules have been created for the circulation of certain types of monetary documents. A clear procedure for issuing and accounting for coupons for the provision of food on a preferential basis in educational institutions has been developed, for example, by the Education Committee of the Government of St. Petersburg ( Order dated 08.06.2009 No.1139-r).
According to this document, educational institutions are supplied with coupons of a single sample. Head of institution
ensures the storage of coupon forms and issues them to the employee responsible for catering, in accordance with the number of students in preferential categories. Forms of coupons are transferred according to the act, the form of which was specially developed and is given in Appendix 3 to this order. This employee issues the completed forms of coupons to the teacher who performs the function of the class teacher, or to the master of industrial training (group supervisor). Issued but not used coupons are returned. All actions with coupons must be recorded in the book for issuing coupons, the form of which is given in Appendix 2 to The procedure for issuing and accounting coupons, approved by Order No. 1139-r.
When providing preferential meals by the educational institution itself, the coupons used for their intended purpose are calculated at the end of each working day and are attached to the cash report. They are stored together with cash register documents for five years and after the expiration of the storage period they are destroyed by order of the head of the institution.
When providing preferential meals at an educational institution, a public catering organization checks the use of coupons on a weekly basis and draws up an appropriate act on their implementation in the form that is given in Appendix 3 to the Procedure for issuing and accounting coupons.
The state educational institution entered into an agreement with a public catering enterprise for the supply of breakfasts and complex lunches for students. The institution paid 120,000 rubles under the contract. Food coupons were received for this amount according to the act of acceptance and transfer. They were credited to the cashier as cash documents. Part of coupons from the cash desk in the amount of 30,000 rubles. was transferred to an accountable person who issued these coupons to students. After the students received food according to these coupons, an act was drawn up in the amount of 30,000 rubles. (attached to the advance report of the accountable person who received the coupons).
According to the Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 171n, the expenses of a state institution for paying for services for organizing hot meals for students are attributed to subsection 226"Other works, services" KOSGU.
These transactions in the accounting of the institution will be reflected in accordance with Instruction No. 162n as follows:
According to the corresponding synthetic accounting code.
Fuel coupons. Consider the option when an institution is provided with fuel and lubricants using coupons: under an agreement, a certain amount of gasoline of the corresponding brand is paid, while the institution receives coupons for which drivers will refuel cars at gas stations.
Received coupons on the basis of the shipping documents of the supplier (invoice, invoices, etc.) are credited as cash documents to the cash desk of the institution, while it is advisable to indicate the brand of gasoline, the series and numbers of these coupons, the face value of the coupons in liters and the cost in the receipt order. coupon in rubles (based on the cost of gasoline specified in the contract and invoice for payment).
As necessary, coupons for the right to receive fuel are issued to drivers or a specially designated employee under the report.
Usually, a special ledger is created for control, in which the movement of coupons is recorded.
The fuel received by coupons is credited as the institution's inventory after the advance report is submitted by an accountable person with supporting documents from the gas station that issued fuel and lubricants in exchange for a coupon.
The budgetary educational institution, as part of the activities to fulfill the state (municipal) task, received from the supplier coupons for 1,000 liters of AI92 gasoline in the amount of 28,000 rubles. The face value of the coupon is 20 liters worth 560 rubles. Accountable person issued
2 coupons, for which it refueled the car, after which it submitted an advance report.
These transactions will be reflected in accounting in accordance with Instruction No. 174n in the following way:
Express payment cards for cellular communications and the Internet. Employees of institutions often use corporate mobile communications or receive compensation for using their own communications for official purposes. A widely used type of payment for mobile communications and the Internet is express payment cards, which are purchased by an institution and must be accounted for as monetary documents.In order for the inspection and tax authorities not to have questions about the legality and expediency of paying the costs of cellular communication, the institution needs to develop an appropriate
statutory provision (internal normative act). This document should contain a list of positions of employees who are eligible to receive mobile payment cards, and the conditions that must be met (for example, employees are paid only for calls made during business hours, or it is still possible to pay for calls made after business hours (during weekend)). It is advisable to prescribe the procedure for employees to confirm their expenses for cellular communications (submission of details of negotiations and an employee’s memo about which calls were official).
An autonomous institution, using funds from income-generating activities, through an accountable person, acquired 100 express payment cards with a face value of 100 rubles. for a total amount of 10,000 rubles. These monetary documents were accepted at the cash desk of the institution. The Deputy Director was issued 3 payment cards for reporting. The accountable person submitted an advance report with corroborative documents.
Expenses for the purchase of payment cards for mobile phones in accordance with the Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 171n are attributed to subsection 221"Communication Services" KOSGU.
In accounting, these transactions will be reflected in accordance with Instruction No. 183n in the following way:
Postage stamps and envelopes with stamps. Despite technological progress, postal services are still relevant and in demand. The organization of postal items is impossible without the purchase of stamps and stamped envelopes, which, according to Instruction No. 157n, must be accounted for as monetary documents. A typical accounting error is the one-time write-off of purchased envelopes and stamps. For example, how can you justify writing off 200 stamped envelopes at once, even if 20 letters were actually sent in a month? They must be accounted for as monetary documents and, as necessary, issued under the report to the persons responsible for sending correspondence, who must draw up an advance report and attach supporting documents to it. Such documents may be a register of sent correspondence, and in case of damage - a damaged envelope attached to the report.Acceptance for accounting and issue under the report of postage stamps and stamped envelopes will be reflected in the accounting as follows:
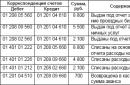
| Government institution (Instruction No. 162n) | State-financed organization (Instruction No. 174n) | Autonomous institution (Instruction No. 183n) |
|||
| Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit |
| Receipt at the cash desk of the institution of stamps and stamped envelopes | |||||
| 0 201 35 510 |
0 302 21 730 0 208 21 660 | 0 201 35 510 |
0 302 21 730 0 208 21 660 | 0 201 35 000 |
0 302 21 000 0 208 21 000 |
| Issuance of stamps and stamped envelopes | |||||
| 0 208 21 560 | 0 201 35 610 | 0 208 21 560 | 0 201 35 610 | 0 208 21 000 | 0 201 35 000 |
According to labor legislation, the amount and procedure for reimbursement of expenses related to business trips of employees, as well as the list of works, professions, positions of these employees are established by a collective agreement, agreements, local regulations. In an educational institution, payment for a ticket can be made to a social pedagogue whose nature of work is associated with traveling (visiting students at their place of residence, trips to participate in meetings of various commissions and prevention councils, etc.).
On the basis of the Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 171n, the expenses of the institution for the purchase of travel tickets for employees whose work is traveling in nature are charged to subsection 222"Transport services" KOSGU.
A government educational institution purchased a bus ticket worth 950 rubles. for September 2013 for a social educator. Payment for the ticket was made by bank transfer at the expense of budgetary funds. The ticket was credited to the cash desk of the institution and issued to the teacher under the report. At the end of the month, the teacher submitted an advance report with an already used travel document attached to it.
In the accounting of a state institution, these transactions must be reflected in accordance with Instruction No. 162n as follows:
Lack of money documents at the cash desk
The procedure for conducting cash transactions with banknotes and coins of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in the territory of the Russian Federation is regulated Regulation No.373-P. According to clause 1.11 of this provision, measures to ensure the safety of cash during cash transactions, storage, transportation, as well as the procedure and terms for checking the actual availability of funds are determined by the legal entity. This means that the procedure for checking the cash desk and cash transactions is established by local regulations, for example, the regulation on internal financial control, accounting policies, and the regulation on cash transactions. During control measures, in addition to the complete recounting of cash at the cash desk, other valuables stored at the cash desk, including monetary documents, are also checked.
To reflect the results of the inventory of monetary documents held at the cash desk of the institution, an inventory list (collation sheet) of strict reporting forms and monetary documents (according to f. 0504086, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 173n) is used.
During the check at the cash desk of a budgetary institution, a shortage of monetary documents was revealed - 2 express payment cards with a face value of 100 rubles each. each purchased with a subsidy for the implementation of the state task. The person responsible for this shortfall has been identified, and the amount of the shortfall has been repaid by him voluntarily in kind.
The institution must record the situation that has arisen in accordance with 86, 87 , 109 , 110 Instructions No. 174n in the following way:
Instructions for the use of the Unified Chart of Accounts for Accounting for State Authorities (Government Bodies), Local Self-Government Bodies, Management Bodies of State Extra-Budget Funds, State Academies of Sciences, State (Municipal) Institutions, approved. Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n.
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 15, 2010 No. 173n “On approval of the forms of primary accounting documents and accounting registers used by state authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state non-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state (municipal) institutions, and guidelines for their application.
The procedure for issuing and accounting coupons for the provision of food on a preferential basis in educational institutions of St. Petersburg.
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of December 21, 2012 No. 171n "On approval of the Guidelines on the procedure for applying the budget classification of the Russian Federation for 2013 and for the planning period of 2014 and 2015."
Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts for budget accounting, approved. Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 6, 2010 No. 162n.
Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of budgetary institutions, approved. Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 16, 2010 No. 174n.
Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of autonomous institutions, approved. Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of December 23, 2010 No. 183n.
Cash documents include:
- paid coupons and plastic cards for gasoline and oils;
– received notices for postal orders;
- stamps;
– state duty stamps;
– other monetary documents.
All monetary documents must be kept at the cash desk of the institution.
Incoming and outgoing cash orders reflecting the movement of cash documents are recorded in the register of incoming and outgoing cash documents (form 0310003), but separately from cash transactions.
Accounting for transactions with monetary documents is kept in the journal for other transactions. Account 00 201 05 000 “Money documents” is intended to reflect operations with monetary documents.
Accounts for accounting for monetary documents do not correspond with account 00 201 04 000 "Cashier", but they are kept at the cash desk, and the cashier is fully liable for them.
In order to control the safety of monetary documents at the cash desk of the institution, a commission appointed by order of the head should conduct an inventory at least once a month. Its results are recorded in the inventory list (collation sheet) of strict reporting forms and monetary documents (form 0504086).
The receipt of cash documents at the cash desk is documented by the entry:
Debit 0 201 05 510 "Receipts of monetary documents" - Credit 0 302 00 000 "Settlements with suppliers and contractors".
The issuance of monetary documents from the cash desk is reflected in the entry:
Debit 0 208 00 000 "Settlements with accountable persons" - Credit 0 201 05 610 "Disposals of monetary documents".
6.3. Accountable persons in budgetary institutions.
Accounting for accountable amounts is kept on separate accounts, depending on the purpose for which the advance is issued, which allows you to control the targeted spending of funds. To receive funds under the report, the employee submits an application indicating the purpose of the advance payment and the period for which the funds are issued.
The issuance of funds under the report is made from the cash desk of a budgetary institution according to an expenditure cash order form 0310002. At the same time, funds under the report can only be issued to an employee of the institution on the basis of an order from the head of the institution. It is prohibited to transfer the received accountable amounts from one employee to another. If the employee has a debt on previously issued accountable amounts, the issuance of a new advance is not allowed.
An employee of an institution who received funds against a report is obliged, no later than three working days after the expiration of the period for which the advance payment was issued, to submit to the institution a report on the amounts spent and make a final settlement on them (letter of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated 04.10.1993 No. 18 "On approval of the procedure for conducting cash transactions in the Russian Federation”). If the accountable person did not submit an advance report within the established time limits or did not return the balance of the advance payment to the cash desk, the budgetary institution has the right to withhold the amount of the debt from the salary of the accountable person who received the advance payment, on the basis of Art. 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). When withholding the amount of the unreturned advance payment from the employee's salary, one should take into account the limitation on the amount of deductions from wages established by Art. 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: the total amount of all deductions for each payment of wages cannot exceed 20%, and in cases provided for by federal laws, 50% of the wages due to the employee.
Account 020800000 “Settlements with accountable persons” is provided to reflect operations for accounting for accountable amounts.
Funds are issued against a report for the payment of wages through distributors, cash payments under concluded agreements, payment of benefits, purchase of securities, etc. The following sub-accounts are used to account for these transactions:
00 208 01 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for wages”;
00 208 02 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for other payments”;
00 208 03 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for accruals for wages”;
00 208 04 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for payment for communication services”;
00 208 05 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for payment of transport services”;
00 208 06 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for utility bills”;
00 208 07 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for payment of rent for the use of property”;
00 208 08 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for payment for property maintenance services”;
00 208 09 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for payment of other services”;
00 208 10 000 “Settlements with accountable persons on gratuitous and non-refundable transfers to state and municipal organizations”;
00 208 11 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for gratuitous and non-refundable transfers to organizations, except for state and municipal organizations”;
00 208 12 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for transfers to other budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation”;
00 208 13 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for transfers to supranational organizations and foreign governments”;
00 208 14 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for transfers to international organizations”;
00 208 15 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for payment of pensions, benefits and payments for pension, social and medical insurance of the population”;
00 208 16 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for payment of benefits for social assistance to the population”;
00 208 17 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for payment of pensions, benefits paid by organizations in the public administration sector”;
00 208 18 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for payment of other expenses”;
00 208 19 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for the acquisition of fixed assets”;
00 208 20 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for the acquisition of intangible assets”;
00 208 21 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for the acquisition of non-produced assets”;
00 208 22 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for the purchase of materials”;
00 208 23 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for the acquisition of securities other than shares”;
00 208 24 000 “Settlements with accountable persons for the acquisition of shares and other forms of participation in capital”.
Consider an example. The labor inspector presented an advance report on travel expenses in the amount of 620 rubles. In doing so, the following entries were made:
Documents confirming the actual purchase of goods or payment for services are attached to the advance report on the amounts spent for economic needs. Such documents include: cash receipts (forms of strict reporting), confirming the receipt of cash from an accountable person; invoices; receipt documents (waybills) confirming the acceptance of material assets from the accountable person to the warehouse of the institution.
Business trip expenses are paid according to the following sub-items of the economic classification of expenses:
212 "Other payments" - expenses for paying per diems;
222 "Transport services" - expenses for paying for travel to the place of business trip and back;
226 "Other services" - expenses for renting a dwelling;
290 "Other expenses" - expenses of a protocol nature in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation during business trips on the territory of foreign states.
Form No. AO-1 "Expense report" contains details that provide for the reflection of accountable amounts both in rubles and in foreign currency. The advance report is filled in by both the accountable person and the accountant of the institution in one copy on paper or on a machine. On the reverse side of Form No. AO-1, the accountable person indicates the list of documents confirming the expenses incurred (travel certificate, receipts, transport documents, cash register checks, sales receipts and other supporting documents), and the amount of actual costs for them. If the expenses are made in foreign currency, in addition to the amount in rubles, the amount in foreign currency is also indicated. The verified report is approved by the head of the institution (authorized person), his position, date and signature with a transcript are put on the front side. After that, the advance report is accepted for accounting. The balance of the unused advance shall be handed over by the accountable person to the cash desk of the organization under an incoming cash order, the overspending is issued to the accountable person under an outgoing cash order. Write-off of accountable amounts of money from the accountable person is made on the basis of the data of the approved advance report.
According to the advance report dated March 30, 2012 No. 50 ( see Attachment) an employee of a budgetary institution was sent on a business trip for 5 days. After returning from a business trip, the employee submitted an advance report, to which were attached: an invoice for hotel accommodation for 4 days for a total of 120 rubles, daily allowance for 5 days for 100.00 rubles. in the amount of 500.00 rubles.
In budget accounting, transactions will be reflected as follows:

The next issue of cash to an accountable person can be made only if the accountable person has a full report on the advance payment previously issued to him.
In the event that the accountable person has the amount of unused funds left, the reissuance of another accountable amount is not allowed. Serious attention should be paid to this provision, since practice shows that often institutions issue accountable amounts without a full account of the accountable person on a previously issued advance.
The procedure and amount of reimbursement of expenses related to business trips are determined by the collective agreement (local normative act).
All travel expenses, except per diems, are recognized in the amount of actual costs, provided they are confirmed by primary documents. Therefore, the employee's travel to the place of business trip and back to the place of permanent work is an expense that is taken into account. Since, in fact, such expenses were incurred only for the purchase of two tickets (for travel to the place of business trip and back to the place of permanent work), it is only necessary to take into account the costs of purchasing these two tickets.
Per diems are paid for the entire time the employee is on a business trip, except for the time when the employee is granted leave, since the leave is classified as rest (Article 107 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
As a general rule, the business trip ends at the moment the employee returns to the place of work. If an employee wishes to receive leave during his business trip and the employer has no objections, then this does not contradict the current legislation. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for the mandatory return of the employee back to the place of work immediately after the business trip is over, provided that the parties have decided otherwise (for example, to provide the employee with leave).
Therefore, if an employee is granted annual leave during the period when he is on a business trip, then by the day the vacation starts, the business trip must end. Therefore, the so-called second part of the business trip, which falls on the period after the end of the vacation, is a new business trip that requires separate registration.
All business transactions of the organization must be documented by supporting documents. Primary accounting documents are accepted for accounting if they are drawn up in the form contained in the albums of unified forms of primary documentation.
The unified forms of documents used when registering business trips were approved by the Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated 05.01.2004 No. 1. In addition to the form No. T-10 “Travel Certificate”, the decree provides for the following unified forms of primary accounting documentation that can be used to issue a business trip:
- No. T-9 "Order (instruction) on sending an employee on a business trip";
- No. T-9a "Order (instruction) on sending employees on a business trip";
- No. T-10a "Service assignment for sending on a business trip and a report on its implementation";
- No. AO-1 "Advance report".
When it comes to several separate business trips, it is necessary to issue these documents for each business trip (business trip before vacation and business trip after vacation).
A travel certificate is a document certifying the time of arrival on a business trip and the time spent on it, at each destination marks are made (on arrival and departure) and certified by the signature of the responsible official, therefore, in a letter dated 05.23.2007 No. 03-03-06 / 2/89 The Russian Ministry of Finance has changed its position. However, the recommendations of the Ministry of Finance of Russia set out in this letter do not apply to the registration of business trips to foreign countries, therefore, a travel certificate is not required. In this case, the fact that the employee is on a business trip will be confirmed by marks in the passport, a copy of which must be attached to the advance report.
In addition to the order for a business trip, an assignment is also issued (form No. 10-a), which describes in detail the purpose of the business trip. A job assignment is necessary when an employee cannot document the effectiveness of his work on a business trip. Form No. 10-a includes the column “Summary report on the implementation of the task”, in which you can describe the work done, but not fixed on paper (search for clients, attending presentations, negotiating). A properly executed job assignment will help demonstrate the practical benefits of the trip and the reasonableness of the costs incurred.
In business practice, accountants everywhere have to draw up such cash transactions as the receipt and issuance of monetary documents. The program "1C: Accounting 8 CORP" (an analogue of the program "1C: Accounting 8", but with advanced features) helps to automate the process of accounting for these assets. How to apply the mechanism incorporated in the program, says M.A. Vlasova, teacher-consultant of the Center for Certified Training of the company "1C: Automation", one of the authors of the book "1C: Accounting 8 CORP: accounting in the parent organization" *.
Note:
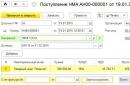
(menu Cash desk -> Receipt of monetary documents
- receipt from the supplier;
- other income.
From whom And Cash documents From whom selectable:
- counterparty from the directory Counterparties Other
- Individuals;
- Other income).
Bookmark Cash documents Cash documents.
For document Receipt of monetary documents Receipt order.
Issuance of monetary documents(menu Cash desk -> Issuance of monetary documents
- Return to supplier;
- Issuance to an accountable person;
- Other issuance.
Bookmark To whom can choose:
- Counterparties Income and expense accounts;
- Individuals;
- offsetting account and subconto to it (if the type of operation is Other issue).
Bookmark Cash documents
For document Issuance of monetary documents printed form provided Withdrawal slip .
What documents are considered "Money"?
Note:
* You can buy the book from the partners of the company "1C". Contact the partner who serves your organization and place an order with the book code - 4601546070173.
Monetary documents include paid railway, air and other transportation tickets, gasoline coupons, vouchers for treatment and rest, postage stamps and other similar papers having a monetary value.
Such assets held in the cash desk of the organization, in the amount of the actual costs of their acquisition, are accounted for on account 50
"Cashier", sub-account 50-3 "Money documents" (Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). It should be noted that the Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts require analytical accounting of monetary documents by their types. In the program "1C: Accounting 8 CORP" special documents, journals and reports have been developed to account for these operations.
Acceptance for accounting of monetary documents is reflected in the document Receipt of monetary documents(menu Cash desk -> Receipt of monetary documents). It includes the following types of operations:
- receipt from the supplier;
- receipt from an accountable person;
- other income.
The document contains two tabs - From whom And Cash documents. Depending on the type of operation on the tab From whom selectable:
- counterparty from the directory Counterparties, an agreement with him (type of agreement Other), as well as an account for accounting for settlements with a counterparty;
- accountable person from directory Individuals;
- offsetting account and subconto to it (if the type of operation is Other income).
Bookmark Cash documents one or more monetary documents are selected from the directory of the same name and their number is indicated. The cost of tickets, coupons, etc. will be filled in based on the data of the directory Cash documents.
For document Receipt of monetary documents printed form provided Receipt order.
The disposal of monetary documents is reflected in the document Issuance of monetary documents(menu Cash desk -> Issuance of monetary documents). The document provides for the following types of operations:
- Return to supplier;
- Issuance to an accountable person;
- Other issuance.
Depending on the type of transaction, the document will contain two or three bookmarks.
Bookmark To whom can choose:
- counterparty to which monetary documents are returned from the directory Counterparties, an agreement with him, as well as an account for accounting for settlements with a counterparty. If there is a difference between the amount of the refund and the value of monetary documents, then it is credited to the income or expense account, which is indicated on the tab Income and expense accounts;
- accountable person to whom documents are issued from the directory Individuals;
- offsetting account and subconto to it (if the type of operation is Other issue).
Bookmark Cash documents the transferred documents are indicated (by choosing from the directory of the same name), their number and the amount of the return.
For document Issuance of monetary documents printed form provided Withdrawal slip. In accordance with the current regulatory documents for accounting for cash transactions in the Russian Federation, the program has developed Report on the movement of monetary documents.
Let's consider the execution of operations with monetary documents using two examples most often encountered in the practice of organizations: the acquisition and issuance of transportation tickets to employees sent on a business trip; purchase of fuels and lubricants by coupons.
Accounting for transportation tickets purchased for business travelers
Currently, there are widespread cases when tickets are purchased not by an employee to whom money is issued for travel expenses on account, but by an organization from a carrier or from an agency that is an intermediary in the distribution of carrier tickets.
Example 1
On January 11, 2010, the organization transferred to the Agency from the current account an advance payment of 14,160 rubles. (including VAT 18%) for the Airline's tickets for the carriage of a passenger.
On January 15, 2010, the Agency's courier brought the tickets purchased by the Agency, the waybill for their transfer and the invoice for the same amount to the organization. Air tickets (2 pieces), on the form of which the cost of transportation is indicated 5,900 rubles, were received on the same day at the cash desk of the organization, and on 01/18/2010 they were issued from the cash desk to an employee sent on a business trip. At the end of the business trip on January 25, 2010, the employee prepared an advance report.
In the program, the transfer of non-cash funds is documented Payment order. The amount transferred to the Agency contains the cost of purchased tickets, which will be credited by the document Receipt of monetary documents(and, therefore, for this amount, the contract with the agency should be of the form Other), as well as payment for the services of the Agency, the acquisition of which will be reflected in the document Receipt of goods and services(which means that an agreement of the form Supplier). This must be taken into account when documents are created on the basis of a payment order. Write-off from current account. If it is clear from the contract with the Agency which part relates to the cost of the service, and which part relates to the cost of the ticket, then two documents should be created for the money transfer operation Write-off from current account: one with operation type Payment to the supplier, another with a view Other settlements with counterparties.
Suppose that it is impossible to determine the indicated shares from the contract (this is the option that will be considered in this article). Then we attribute the entire amount of the prepayment to the contract of the form Supplier(Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Write-off of money from the current account
In accounting, the document will post:
Debit 60.02 Credit 51 - 14,160 rubles. - for the amount of advance payment to the Agency.
Acceptance of transportation documents for accounting is reflected in the debit entry of sub-account 50.03 in correspondence with the credit of account 76.09. Executes the transaction document Receipt of monetary documents with type of operation Receipt from supplier(this creates and selects a contract of the type Other). The evaluation of tickets at the box office must correspond to the cost of transportation, since it is this amount that can be received from the carrier in the event of termination of the contract issued by the ticket.
The organization paid not only the cost of transportation, but also the cost of ticketing services. The agency has completed the provision of its service by delivering tickets with the required characteristics to the customer, and it is at this moment that a document is drawn up in the configuration Purchase of goods and services for the cost of the service. Since the service has been received, the VAT included in its cost can be deducted. To do this, you need to enter information about the Agency's invoice (on the tab or via the hyperlink Invoice).
The postings that the document will make in accounting are shown in Fig. 2.
Rice. 2. Accounting entries for the service purchase document
After the transactions, two debts remain in the accounting - accounts receivable on account 60.02 (prepayment) and accounts payable on account 76.09 for the amount of tickets received.
These debts relate to contracts of different types. You need to set off these debts using a document Debt Adjustment.
Before sending an employee on a business trip, he is given an advance from the cash desk of the organization - in this case in the form of a transportation ticket. This operation is documented Issuance of monetary documents(Fig. 3).

Rice. 3. Issuance of monetary documents to the account
Upon returning from a business trip, the employee is obliged to submit a report on the amounts spent to the accounting department of the enterprise within three working days and make the final settlement on them (clause 11 of the Procedure for conducting cash transactions in the Russian Federation, approved by the Decision of the Board of Directors of the Central Bank of Russia on September 22, 1993 No. 40).
The accountant, on the basis of the documents submitted by the employee, draws up an advance report, on the tab Advances which the accountable amounts are indicated, and on the tab Other- payment for the services purchased by the employee, which include travel expenses to and from the destination.
Indicating the amounts for which the employee reports, on the tab Advances document Advance report you need to select the registrar that issued the accountable amounts. Among others, it may be a document Issuance of monetary documents. Airline details are entered on the bookmark Other.
The company that performed the transportation may present the buyer with VAT included in the price of the service. The amount of VAT paid by the taxpayer on travel expenses to the place of a business trip and back, accepted when calculating corporate income tax, is deductible (clause 7, article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The right to deduction arises after the approval of the employee's advance report by the head of the organization.
If at the same time the carrier presented an invoice, then the organization can accept VAT deductible on the basis of the presented invoice. To do this, check the box (checkmark) in the column SF presented advance report, specify the date and invoice number, and then "post" or "record" the advance report. The invoice will then be generated automatically. In the future, information about the presented VAT amount will be included in the document Formation of purchase book entries.
If there is no invoice, then VAT, allocated as a separate amount in the ticket form, can also be deducted, since according to paragraph 10 of the Rules for maintaining accounting logs of received and issued invoices, purchase books and sales books when calculating value added tax , approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 02.12.2000 No. 914, when purchasing services for the transportation of employees to the place of a business trip and back, the strict reporting forms (or their copies) filled out in the prescribed manner (or their copies) with a separate line for the amount of VAT issued to the employee and included in the business trip report.
Since, in general, the presence of an invoice is one of the mandatory conditions that must be met when accepting VAT for deduction, the program will not allow a deduction if information about the invoice is not entered into it. However, such a special document as a strict reporting form (BSO) for VAT purposes is not provided in the configuration, therefore, under the document Invoice received should be understood directly as an invoice, and BSO.
Thus, if VAT is deductible on the basis of a transportation ticket (in the absence of an invoice), you must put in the column SF presented a flag indicating that a strict reporting form has been presented, indicate the date of the BSO, and in the column SF number you can specify not only the number of the form, but also its name (Fig. 4).

Rice. 4. Travel expenses report. VAT on tickets is deductible
After performing these operations, the program in the printed form of the purchase book indicates a strict accountability form, and the requirement of Decree No. 914 will be fulfilled.
Accounting for gasoline coupons
There are various options for refueling a car with fuel and lubricants. At some companies, fuel for refueling a car is purchased by drivers, who are given money for this under a report. Other organizations, having made a transfer to the supplier, "acquire" from him special coupons for petroleum products. Subsequently, drivers receive these coupons from the fuel supplier and refuel vehicles with them.
Example 2
For the purchase of 100 coupons for gasoline, the organization transferred 23,600 rubles, including VAT - 3,600 rubles. Coupons were credited at the box office. For refueling vehicles in January, 60 coupons were handed over to the driver, for each of which you can get 10 liters of gasoline. According to the report submitted at the end of the month, gas stations dispensed 500 liters of fuel for 50 coupons in January.
An agreement of the form must be drawn up with the supplier of gasoline Supplier, because in the document Write-off from current account(type of operation Payment to the supplier) it will be selected as the contract under which funds are transferred. The supplier's debt that arose in this case on account 60.02 (in correspondence with account 51) must be recorded in the organization's records until the receipt of fuels and lubricants.
The posting of gasoline coupons (cash documents) to the cash desk is carried out by a document Receipt of monetary documents with type of operation Receipt from supplier. In this case, a contract of the form Other and the account of settlements - 76.09 can be indicated.
It should be noted that the supplier's contracts can be combined into a group, which will be understood as a real contract signed with the supplier.
Bookmark Cash documents document Receipt of monetary documents coupons received at the cash desk of the organization are selected (Fig. 5). When posting the document, an account payable to the gas station arises on account 76.09.
Rice. 5. Posting to the cashier coupons for gasoline
The issuance of coupons to drivers from the cash desk of the organization is registered by a document Issuance of monetary documents. In this case, the type of operation B is selected. issuance to an accountable person.
At the end of the month, employees of the organization who were issued coupons report on their spending. For this purpose, the program compiles an advance report, on the tab Advances which the accountable amount is selected according to the document that registered the issuance of coupons (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Selection of the document that issued the issuance of monetary documents
Since a common document is drawn up with the gasoline supplier, which confirms the purchase and sale of fuels and lubricants for the whole month, and a single invoice is issued for it, it is better to register for each advance report not the receipt of gasoline, but the repayment of the debt. To do this, fill in the bookmark Payment by selecting a counterparty and an agreement of the type Supplier. When conducting an advance report, the debt on account 60.02 will increase.
The posting of gasoline is made by a document Receipt of goods and services. With its help, data on the invoice presented to the organization by the supplier is also entered.
In the future, the accountant calculates how much gasoline was consumed by drivers according to the norms and in excess of the norms. Gasoline used within the norms is written off as expenses accepted for taxation purposes, and spent in excess of the norms - as expenses not taken into account when calculating income tax. In both cases, the write-off of fuel and lubricants for expenses is recorded by a document Invoice claim.
After the operations carried out in the accounting records of the organization, debts related to the purchase of fuel and lubricants will remain under contracts of two different types: debit on account 60.02 and credit on account 76.09.
Since the gasoline settlement operations are completed, the debts can be settled by offsetting using the document Debt Adjustment.