Own funds of the enterprise include reserve, authorized, additional capital. These are the main elements through which the financing of the company's production activities is carried out. Let us consider further in detail what constitutes the reserve capital of the organization.
General information
To compensate for losses in the course of financial and economic activities, companies provide for a reserve fund. The capital is directed to the payment of accounts payable and deductions to investors in the event of a lack of profit for the reporting year. The presence of these funds acts as a kind of guarantee for the stable operation of the company.
Legal aspect
The obligation to create reserve capital is provided for in Federal Law No. 208. This requirement applies to JSCs and joint corporations. LLCs, cooperatives and other commercial structures can create such a reserve of funds if it is provided for in the founding documents. The reserve capital of a joint-stock company can be used to cover losses, redeem bonds, buy back securities in the absence of other assets. These funds are not allowed to be used for other purposes.
The order of formation
The value of the stock is determined in the constituent documents of the enterprise. Authorized and reserve capital are two interrelated categories. Depending on the size of the first, the value of the second is determined. Thus, in accordance with the legislation in a JSC, the reserve capital cannot be less than 15% of the authorized capital. For enterprises with foreign investment, this figure increases to 25%. The formation of reserve capital within the limits of the above restrictions is carried out by reducing taxable income. In this case, the amount of deductions should not be more than half of this profit. According to the Federal Law that regulates the activities of JSCs, a requirement is provided in accordance with which a reserve is formed. Its size must be at least 5% of the authorized capital. In this case, the upper limit may be greater than the specified indicator, since this limitation is not provided for in regulatory acts. The reserve capital in a joint-stock company is formed at the expense of annual mandatory deductions until it reaches the value specified in the constituent documents.

Important point
Today, many JSCs have a reserve capital of less than 2-4% of the authorized capital. At the same time, there are no violations of the requirements of the law or the provisions of the constituent documentation. The thing is that these companies over the past few years have revised the size of their authorized capitals and increased them at the expense of additional ones. In some cases, the indicators increased by 10, and in others - more than a hundred times due to the increase in the value of revalued property. In this regard, the already increased amount of authorized funds should be taken as the basis for calculating the indicator of 15%. The financial reserve for other enterprises is created in a different order. The main source from which the funds come to the reserve capital is retained earnings remaining at the disposal of the enterprise.
Reporting: general rules
Accounting for additional and reserve capital is carried out in accordance with the prescribed rules for maintaining the relevant documentation. The size of the reserve is taken into account when making decisions and carrying out business operations in the JSC. The use of these funds is within the competence of the Supervisory Board/Board of Directors. This provision is provided for in Art. 65 of the said Federal Law No. 208. The amount of the fund is taken into account when:
- Deciding on declaring/paying dividends.
- Increase in the authorized capital.
- Payment of dividends.
- Acquisition of placed securities, including certain preferred ones.

Reserve capital: postings
The stock formation is shown as follows:
- db ch. "Losses and profits" (99), cd sc. "Uncovered loss (retained earnings)" (84) - reflects the amount of net income received for the reporting period by the closing entries for December.
- sch. 84 (debit), c. 82 (credit) "Reserve capital" - contributions to the reserve from net profit were made.
The directed amounts do not reduce taxable income and are not included in tax expenses. In some cases, it becomes necessary to change the reserve capital. The account will reflect the transactions made only if these adjustments are made to the constituent documents and registered in accordance with the established rules. In reporting, such operations are shown as follows: dB sch. 82, cd sc. 84 - the reserve was reduced to the amount provided for in the constituent documentation.

Line 430 of the balance reflects the balance of the reserve capital at the end of the reporting period. It can be shown both in general and in the following types:
- Created in accordance with the law.
- Formed in accordance with the constituent documents.
Features of the direction of funds
Accounting for the reserve capital used to cover the company's losses, redeem bonds and buy back securities is carried out and reflected in the balance sheet separately. According to the methodological recommendations containing provisions on the procedure for compiling reporting indicators when considering the results of activities for the period and resolving issues related to sources of financing costs, the reserve funds can be used for these purposes. In accordance with paragraph 4, Art. 88 of the Federal Law No. 208, the company's annual accounts must be preliminarily approved by the board of directors by a supervisory body or by a person who solely performs the functions of an executive body. This must be done no later than 30 days before the day of the annual general meeting of participants. The decision to direct the funds constituting the reserve capital to pay off losses is made after the approval of the reporting. Such use of funds qualifies as an event occurring after the end of the period. 
Bond redemption
In accordance with Art. 816 of the Civil Code, in the cases provided for by law and other regulatory acts, it is allowed to conclude a loan agreement through the issuance and sale of securities. Long-term and short-term fundraising in this way is accounted for on the account. 66 and ch. 67 separately from non-bond finance. If the placement of securities is carried out at a cost exceeding their nominal price, then entries are made at Db sch. 51 and others in correspondence with accounts 67, 66 (for the nominal value) and 98 (for the difference). The amount that has been charged to 98, is written off evenly over the period of circulation of bonds to the account. 91, subch. 91-1, sub. 91-2. Debt on loans and credits is reflected taking into account interest payable at the end of the period. The latter act as operating expenses of the company. They are counted on 91. The redemption of bonds is the payment of the nominal value and a fixed percentage of it or the property equivalent to the holder within the established period. 
Redemption of securities
According to Art. 101 SC JSC can reduce its authorized capital by acquiring a part of shares in order to reduce their total number. This is allowed if this possibility is provided for in the constituent documents. The acquisition procedure, as well as restrictions on the purchase of placed securities, are established in Federal Law No. 208, Art. 72, 73. Changes regarding the reduction of the authorized capital are made to the constituent documentation under paragraph 1, art. 12 of this law on the basis of a decision taken at the general meeting of participants. Own securities redeemed from the founders are reflected in Db account. 81. At the same time, the amount of actual expenses related to the redemption in correspondence with Kd of accounts for accounting for financial resources is indicated. Cancellation of securities is reflected in Kd account. 81 and db sc. 80 after the company has completed all the procedures provided for in such cases. The difference between the actual costs of redemption and the nominal value of securities arising on the account. 81, transferred to sc. 91 "Other costs and income". The lines will be as follows:
- db ch. 81, cd sc. 50 - redemption of own shares.
- db ch. 80, cd sc. 81 - reduction of the authorized capital through the redemption of repurchased securities.
- db ch. 91-2, cd sc. 81 - reflection of the difference between the cost of the redemption and the nominal price of the canceled shares.

Procedure for LLC
Such companies cannot make decisions on the distribution of profits between participants:
- If the value of net assets is less than the authorized and reserve funds or will decrease after such a decision is made.
- Until payment of the real value of the share (its part) of the founder.
- Until payment of the authorized capital in full.
- If there are signs of insolvency (or if they appear after the decision is made).
The legislation does not oblige an LLC to create a reserve capital. But they can form it if it is provided for in the constituent documentation. Since this procedure for an LLC is not regulated by law, there are no restrictions either on the size or on the procedure for creating a financial reserve. According to the law, the amount by which the authorized capital is increased at the expense of the company's property should not be higher than the difference between the value of the net asset and the size of the reserve and authorized funds.
Account 82 "Reserve capital" is intended for generalization of information on the state and movement of reserve capital.
Deductions to reserve capital from profit are reflected in the credit of account 82 "Reserve capital" in correspondence with the account "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)".
The use of reserve capital is accounted for in the debit of account 82 "Reserve capital" in correspondence with the accounts: "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" - in terms of the amounts of the reserve fund directed to cover the organization's loss for the reporting year; "Calculations on short-term credits and loans" or "Calculations on long-term credits and loans" - in terms of the amounts allocated for the redemption of bonds of a joint-stock company.
Account 82 "Reserve capital"
corresponds with accounts
Chart of accounts application: account 82
- Audit program
On account of the contribution to the authorized capital; -journals-orders and statements of accounts 75 ... "Settlements with founders", 80 "Authorized capital", 81 "Own ... shares (shares)", 83 "Additional capital", 82 "Reserve capital", general ledger ; -financial statements. RD...
- The procedure for filling out the balance sheet in a general form. Example
Which is taken into account on account 83 "Additional capital". Additional capital (without revaluation ... be reflected in the line above. Reserve capital. The balance of the reserve fund is indicated on line 1360 ... assets). Line 1360 "Reserve capital" = Kt 82. Line 1370 "Unallocated ...; Authorized capital (share capital, authorized fund, contributions of comrades)" is equal to the credit balance of the account .... Line 1360 "Reserve capital" - the credit balance of account 82. In our case, this is ...
- The procedure for completing the balance sheet in a simplified form. Example
Lines. In the first line "Capital and reserves" indicate the total ... reflected in sec. III "Capital and reserves" of the usual form ... dividend payments, contributions to authorized capital, etc. Pay attention... Dt 50 15,000 Kt 82 10,000 Dt 51,250 ... now the balance sheet liability. Authorized and reserve capital, as well as retained earnings are reflected ... on one line "Capital and reserves". Amount... account 60 credit balance + account 62 credit balance + account 69 credit balance + credit...
- Audit of the annual financial statements of organizations for 2018
16 February 2005 No. 82 additional capital of the organization. Disclosure of data on... the name and characteristics of balance sheet account No. 40824 “Escrow accounts of individuals, individuals... by shareholders, participants for an increase in the authorized capital of a credit institution have been specified. The amounts specified...
- The immediate outlook for the ruble has become more dependent on capital flows
Accounts of the balance of payments - direct investment inflows and capital inflows ... increasingly dependent on capital flows - its weakening now ... a barrel). The traditional deterioration of the current account in the second quarter... to $83.4 billion from $82.4 billion in the first quarter... sales of foreign currency from the Reserve Fund, a decrease in capital outflows from the banking sector... shocks and a sharp increase in capital outflows. “The balance of payments is everything... the higher the current account surplus, the higher the capital outflow), we bet on...
Banks account 51 "Settlement accounts" (instead of accounts 51 "Settlement accounts" ... capital account 80 "Authorized capital" (instead of accounts 80 "Authorized capital", 82 "Reserve capital ...", 83 "Additional capital" ... ; ); to account for financial results, an account ...
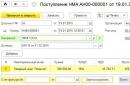
Accounting reference An increase in the net assets of an enterprise by contributing property (property rights) to the shareholders of the company can also be reflected as an increase in the reserve fund. Posting in this case: Dt Kt Description of the operation 75 82 Reflected the contribution of funds to the reserve capital by shareholders (members) Example of formation by transferring funds by shareholders The participants of the company at the meeting decided to contribute 10,000,000 rubles to the reserve fund. To reflect this operation, transactions were created: Dt Kt Description of the operation Amount Document 51 75 Reflected the receipt of DS from shareholders 10,000,000 Bank statement 75 82 Reflected the formation of a reserve from shareholders' contributions 10,000,000 decision of the board of directors of the JSC or its other governing body.
Postings on account 82
Gratuitous receipts98-3 - Future receipts of debts for shortages identified in previous years98-4 - Difference between the amount to be recovered from the guilty parties and the cost of missing valuables99 - Profits and losses Kt 001 - Leased fixed assets002 - Inventory accepted for safekeeping003 — Materials accepted for processing004 — Goods accepted for commission005 — Equipment accepted for installation006 — Strict accounting forms007 — Debts written off at a loss from insolvent debtors008 — Security for obligations and payments received009 — Security for obligations and payments issued01 — Fixed assets001-11 — Disposal of fixed assets 010 - Depreciation of fixed assets 011 - Fixed assets leased out 012 - Intangible assets received for use 013 - Inventory and household.
Accounting for reserve capital (account 82). wiring
Salary for April: do not make a mistake in the date of transfer of personal income tax due to the May holidays This year, the first "portion" of the May holidays will last 4 days (from April 29 to May 2 inclusive). If your company has a payday on the 1st or 2nd, you will have to pay your April salary ahead of schedule - April 28th. On the same day, you need to withhold personal income tax.< …
It is better to pay off tax debts before May 1. Otherwise, potential and existing counterparties will see information that the company owes the budget for a whole year.< … Главная → Бухгалтерские консультации → Бухгалтерский учет Актуально на: 26 января 2017 г. Требование осмотрительности в бухгалтерском учете предполагает бОльшую готовность к признанию расходов и обязательств, чем доходов и активов (п.
6 PBU 1/2008). And the creation of reserves in accounting is due precisely to this requirement.
Reserves in accounting
Postings The financial result is accumulated on an accrual basis over 12 months. With these funds, taxes and fees are paid first of all, then the funds provided for by the charter are formed. The rest of the amount is net income. It is refinanced or allocated to meet the needs of the organization.
Let's consider typical records that are formed in correspondence with account 84 "Retained earnings". Wiring:
- DT84 KT51 - part of the expenses was paid from net profit.
- DT84 KT70 - a bonus was paid to employees.
- DT84 KT80(83) - the amount of the authorized (additional) capital has been increased.
- DT73 KT84 - loss coverage at the expense of employee contributions.
- DT80 KT84 - the authorized capital was changed to the amount of net assets.
Payment of dividends The meeting of shareholders is responsible for the approval of annual reports.
Accounting for the formation and use of retained earnings
Info
We will tell you about what reserves are created in accounting in our consultation. What reserves are Reserves created in accounting can be divided into 3 groups:
- Reserve capital;
- estimated reserves;
- provisions for estimated liabilities.
All these reserves differ both in terms of the source of formation and the order of reflection in accounting. Reserve capital The reserve fund (capital) is formed by organizations from profits in accordance with their constituent documents and is used to cover losses, as well as for other purposes.
1 st. 30 of the Federal Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ, paragraph 1 of Art. 35 of the Federal Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ). Reserve capital is accounted for on account 82 “Reserve capital” (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
Keeping records of reserve capital on account 82 (postings)
In the conditions of normal functioning, the organization, after paying all expenses and tax liabilities, has a certain amount of money left. This retained earnings is usually reinvested in the organization. The owners decide how the funds will be used in the future.
Attention
Profit The main indicator of the company's activity is the change in the cost of capital. It is displayed on account 99 "Profit and Loss". For DT, losses are recorded, and for CT, income. Comparison of the results forms the financial result of the organization.
Consider an example. The turnover of account 99 for the 1st quarter amounted to: 10,000 rubles. for diesel fuel and 12.5 thousand rubles. by CT. The final balance is calculated according to the formula: Balance at the beginning of the period + CT turnover - DT turnover = 0 + 12.5 - 10 = 2.5 thousand rubles. Movement for the 2nd quarter: for diesel fuel - 15 thousand rubles, for CT - 13.5 thousand
rub. Balance \u003d 2.5 + 13.5 - 15 \u003d 1000 rubles.
Retained earnings: postings
Video lesson "Accounting for reserve capital on account 82" Download the presentation for the video lesson "Accounting for reserve capital for account 82: postings, examples" in PDF format How is reserve capital formed? After the calendar year is over, all final entries are reflected, reports for the year are compiled - a meeting of the participants (founders) of the company is held, at which it is decided how the net profit will be distributed: for the payment of dividends, for the formation of a reserve, etc. As above it was it is said that for joint-stock companies the formation of reserve capital is a mandatory procedure, and it is established that the amount of reserve capital should be at least 5% of the amount of authorized capital. The specific amount of the reserve for each individual organization is determined by its constituent documents (charter).
Due to retained earnings increased reserve capital posting
No interest is charged on unpaid dividends. Non-received amounts are accounted for as part of other income of JSCs: DT 75 (76) KT 91. Reserve capital To finance losses, redeem bonds, buy back their own securities, JSCs create a special fund. Its minimum size is 5% of the authorized capital. The law provides for an annual transfer of funds in the amount of 5% of net profit.
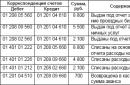
As in the case of article 84 "Retained earnings", account 82 "Reserve capital" is passive. That is, a decrease in the amount of funds is displayed on a debit, and an increase on a credit. Consider typical wiring:
- DT84 KT82 - fund formation.
- DT82 KT84 - loss write-off.
- DT82 KT66(67) - redemption of bonds.
- DT84 KT84 - covering the debts of previous years.
Acquisition of property Retained earnings may be used to purchase intangible assets.
Increased reserve capital at the expense of retained earnings
These operations are displayed in the BU with the following postings:
- ДТ84.1 КТ75.2 - payment of income.
- DT84.1 KT82 - replenishment of the reserve fund.
- DT84.1 KT84.4 - coverage of losses.
Reporting Retained earnings in the balance sheet is: 1) in quarterly reporting:
- balance on account 99 "profit and loss" plus / minus;
- balance on account 84 "retained earnings (uncovered loss)" minus;
- balance on account 84 “retained earnings (uncovered loss)” (in terms of interim dividends accrued in the reporting period);
2) in the annual reporting: account 84. If the enterprise did not have a financial result for the previous years or intermediate accrued income of the owners, then the value of lines 1370 of the balance sheet and 2400 of form No. 2 are the same. Sometimes the organization in the interreporting period is forced to adjust the balance sheet.
By studying the features of account 82, one can make such a description of it. This is the account:
- passive, since it takes into account the sources of the enterprise's property; RC is one of the constituent parts of the capital of a joint-stock company and, like all sources for assets, is reflected in the liabilities side of the balance sheet;
- balance sheet, because its indicators are reflected in the balance sheet;
- stock, since it is intended to account for the sources of formation of funds belonging to the joint-stock company - the capital of the company;
- the main one, because it is designed to control the state and movement of the sources of formation of the company's property (in this case).
You can read about the sources of capital formation in our article “The main sources of equity capital formation”.
Reserves for estimated liabilities include a reserve for vacation pay, a reserve for warranty repairs and other similar reserves (PBU 8/2010). Provisions for estimated liabilities are reflected in the account of provisions for future expenses. We will show the accounting entries that are made when creating and using a reserve for future vacation pay: Operation Debit account Credit account Formed (adjusted) a reserve for vacation pay 20 “Main production”, 26 “General business expenses”, 44 “Sale expenses”, etc.
96 "Reserves for future expenses" The funds of the reserve for the payment of vacation pay to employees (compensation for unused vacation) were used 96 70 "Settlements with personnel for wages" Insurance premiums from vacation payments were accrued at the expense of the reserve 96 69 "Calculations for social insurance and security" Subscribe to our channel in Yandex.
For enterprises of other forms, the creation of a reserve fund is possible at the choice of management. Reserve capital may include:
- employee corporatization fund;
- reserve fund;
- fund for dividends on preferred shares;
- and others.
This fund is intended to cover the losses of JSCs, as well as to settle bonds and shares in the absence of other sources. The reserve fund may not be used for any other purposes.
Reserve capital is formed by deductions from net profit. The annual amount of deductions is set by the management of the JSC, this rate cannot be less than 5%. The capital of the reserve fund in the preparation of financial statements is included in the equity capital of the enterprise.
How reserve capital is formed Reserve capital is formed by posting Dt 84 "Retained earnings (loss)" - Kt 82 "Reserve capital".
When creating your own business, you must follow a series of consistent steps, the order of which is monitored by the relevant authorities. To date, the preparation of everything necessary can be done both independently and with the help of legal services. You can pay a certain amount, and in a short time, a team of lawyers will prepare the entire package of documents without too much fuss.
To create your own business, you need to solve a number of issues, without which no enterprise can function, no matter what form of ownership it represents.
One of the first tasks that needs to be solved in the first place is to form the authorized capital.
What is authorized capital
The authorized capital is a certain amount of money or a cash equivalent that allows investors to compensate in case of failure the costs of the organization's activities. The amount of capital depends on the type of economic activity of the company and has a certain value.
Capital can be expressed not only in the amount of money, but also in the form of real estate, shares, material values. Since at the initial stage a bank account of the organization is opened, during the first month half of the total amount of the authorized capital is paid to it.
The concept of reserve capital
Reserve capital is a certain part of the main authorized capital, from 5 to 25% - depending on the type of organization. Its amount is set in the company's charter, the creation of which is mandatory.
The reserve capital is intended to store part of the profits received and its subsequent distribution for the purchase of shares, as well as the repayment of debts, if any. The tradition of forming a reserve capital originates from Western practice, where it has long been customary to protect your business from financial insolvency.

Not all organizations require a capital reserve. For example, a limited liability company and individual entrepreneurship are not required to create such capital, while it is mandatory for a joint-stock company.
Formation of reserve capital
The amount of reserve capital is not accumulated immediately, but over a certain period of time. The reserve capital is formed at the expense of the organization's profit, while a part of the net profit is deducted to the reserve capital fund until the amount specified in the authorized capital is received. In order to get the amount for deductions to the fund, they reduce net profit, that is, they use part of the profit after paying the necessary taxes.

In addition to the fact that there is a mandatory part of the profit that goes to the formation of the reserve (mortgaged both by the legislation and the charter of the enterprise), there are other sources of replenishment of the reserve fund. These are estimated reserves, according to the management of the enterprise, minus the estimated costs and income (subject to the stability of the production process).
Speaking about the accounting side of this part of the budget, it is worth saying that the concept of reserve capital - accounting entries - is associated with a separate account with a similar name. The reserve capital, whose account is 82, allows you to control settlement operations for this part of the budget.
The amount of annual income to the reserve fund should be a share of more than or equal to 5% of the net profit from the activities of the enterprise.
By the size of the reserve capital, one can judge how firmly the company feels in the financial market, its success and profitability.
Use of reserve capital
There is a list of expenditure transactions for which reserve capital can be spent:

If an organization wants to reduce its authorized capital, this can be done by buying back bonds and shares from shareholders with their subsequent redemption, for which it is also allowed to use funds from the reserve fund.
Reserve capital for various types of ownership
The formation of a reserve for various types of economic activity has its own characteristics. The reserve capital of a joint-stock company is formed in the amount of at least 5% of the authorized capital. In the event that a foreign investment contribution is involved in the activities of the organization, the amount of the reserve increases to 25%. At the same time, joint-stock companies also have a minimum threshold for the value of the reserve fund.

Every year it is necessary to deposit a certain amount, the minimum figure is 5% of net profit, while the minimum transfer is determined by law. It is for this type of activity that the designated purpose of the reserve capital is determined.
For a joint-stock company and a joint venture, the creation of a reserve is mandatory, for individual entrepreneurs and a limited liability company it is not necessary, therefore, you can spend the funds accumulated in the reserve at your discretion.
Control over the formation of reserve capital
For a joint-stock company at the end of each year, it is mandatory to provide financial statements on the activities of the company, so it is easy to determine the amount of transfers to the reserve fund and the use of funds from it.
Since the reserve capital is formed from the profit of the organization to which the shareholders and investors are related, the distribution of profit (including the use of the reserve capital) must be agreed upon at the meeting of shareholders.

An accounting report on the activities of the organization is provided after the reporting period, in connection with which the question may arise of how the budget plan for the next year is laid. To resolve this issue, an organizational meeting of shareholders is held, where reporting documentation is provided. In parallel, the reserve is planned for the next reporting period.
Increasing the amount of reserve capital
The rules do not prohibit an increase in the size of the reserve capital, and this can be done at any stage, even until the amount of the reserve capital reaches the threshold of 5%.
The size of the reserve can be increased by holding a meeting of shareholders and making this decision. After that, it is necessary to make all changes to the bylaws.

There is a relationship between the value of the reserve and authorized capital, therefore, it must be taken into account that, by increasing the amount of the reserve capital, it is necessary to increase in proportion to the amount of the total (authorized) capital.
Accounting statements on reserve capital
The allocation of funds to the fund, as well as the expenditure of money from the fund to cover needs and debts, should be reflected in the accounts for uncovered losses, as well as for long-term and short-term loans.
Thus, one of the mandatory conditions for the formation of a joint-stock company or joint venture is the formation of the main authorized and reserve capital. There are certain rules for creating a reserve fund, which are regulated by law. The receipt and expenditure of funds from the reserve fund should be reflected in the accounting records, as well as budget planning for the next year.
reserve capital accounting
Reserve capital represents the insurance capital of the enterprise, intended to compensate for losses from economic activities, as well as to pay income to investors and creditors in case there is not enough profit for these purposes. The funds of the reserve capital act as a guarantee of the uninterrupted operation of the enterprise and the observance of the interests of third parties. The presence of such a financial source gives the latter confidence in the repayment of the company's obligations.
The formation of reserve capital can be mandatory and voluntary. Currently, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, which determines the procedure for the activities of joint-stock companies and enterprises with foreign investments, as well as with tax legislation, these organizations must form reserve capital on a mandatory basis. At their discretion, enterprises of other forms of ownership can also create it, if this is provided for by their constituent documents or accounting policies.
Accounting for the formation of reserve capital should provide information necessary to monitor compliance with its upper and lower limits. In all cases, the maximum amount of reserve capital cannot exceed the amount determined by the owners of the enterprise and fixed in the constituent documents. At the same time, its minimum size is also legally established for joint-stock companies and joint ventures.
From January 1, 1996, after the Law "On Joint Stock Companies" comes into force, they are obliged to create a reserve capital of at least 15% of the amount of the authorized capital and form it by annual deductions in the amount of at least 5% of net profit until the amount determined by the charter is reached. society.
The minimum amount of the reserve capital of organizations with foreign investments in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation should not exceed 25% of the authorized capital.
Since January 1, 1995, only undistributed net profit has been the source of formation of reserve capital for enterprises of all organizational and legal forms.
To obtain information on the availability and movement of reserve capital, the new chart of accounts provides for account 82 "Reserve capital". The formation of reserve capital at the expense of undistributed net profit is reflected in the debit entry of account 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" in correspondence with account 82 "Reserve capital".
The new chart of accounts provides for the use of reserve capital to repay issued bonds on received short-term and long-term loans and to cover losses from business activities.
When redeeming bonds of loans, an entry is made in accounting:
Dr. c. 82 "Reserve capital", Set of accounts. 66 "Calculations on short-term credits and loans", Kt sc. 67 "Settlements on long-term credits and loans".
The use of reserve capital to cover losses is reflected in the entry:
Dr. c. 82 "Reserve capital", Set of c. 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)".
8.accounting for additional capital
To account for the amounts of additional capital and summarize information about their accumulation and use, account 83 "Additional capital" is intended without division into sub-accounts.
Analytical accounting for this account is carried out according to the sources of its formation and directions of use. The sources of formation are:
increase in the value of property by revaluation and due to capital investments;
share premium;
positive exchange differences resulting from the contribution of foreign currency to the authorized capital of the enterprise;
funds allocated from the budget and used to finance long-term investments;
funds of the enterprise aimed at replenishment of working capital.
Funds from gratuitous receipt of property are now reflected in deferred income on account 98 "Deferred income".
As a result of the revaluation of fixed assets, the amount of additional capital may change in the direction of not only an increase, but also a decrease.
In accounting, a change (increase) in the initial cost of fixed assets, equipment for installation is reflected in an entry on the credit of account 83 "Additional capital" in correspondence with accounts 01 "Fixed assets", 03 "Profitable investments in tangible assets", 07 "Equipment for installation" . In this case, the difference between the replacement and initial amount of depreciation of fixed assets is taken into account in the debit of account 83 "Additional capital" in correspondence with account 02 "Depreciation of fixed assets".
If property is accepted for accounting as a result of capital investments at the expense of undistributed net profit, an entry is made:
Dr. c. 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)",
Share premium is generated in open joint-stock companies and represents the amount of the excess of the sale price of shares over the nominal value during an open subscription. Upon receipt of such income in accounting, an entry is made on the credit of account 83 "Additional capital" in correspondence with account 75 "Settlements with founders", subaccount 1 "Settlements on contributions to the authorized (share) capital".
The share premium that arose during the formation of the authorized capital of joint-stock companies is considered only as additional capital, it is not allowed to direct it to consumption needs.
According to the Accounting Regulation "Accounting for Assets and Liabilities Denominated in Foreign Currency" (PBU 3/2000), exchange differences associated with the formation of the organization's authorized capital are subject to addition capital. In this case, the exchange rate difference means the difference arising between the official foreign exchange rates quoted by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of its actual contribution to the authorized capital and on the date of state registration of constituent documents. In modern conditions, it is, as a rule, positive and, therefore, is considered as an inflationary source, taken into account in the composition of additional capital.
In accounting, a positive exchange rate difference arising from the introduction of foreign currency into the authorized capital of an enterprise is reflected by an entry on the credit of account 83 "Additional capital" in correspondence with account 75 "Settlements with founders", subaccount 1 "Settlements on contributions to the authorized (share) capital ".
Appropriations received from the budget of any level, which are spent by the enterprise to finance long-term investments, join the additional capital.
The funds received from the budget are first credited to a special bank account, from which they are then debited to cover the costs incurred in accordance with the investment program of the enterprise. Further, the spent amount of budgetary appropriations is included in the composition of additional capital with an accounting entry:
Dr. c. 86 "Target financing",
Set of c. 83 "Additional capital".
The basis for such accession can only be the fact that budgetary funds are used for their intended purpose.
Additional capital can be replenished at the expense of funds allocated for replenishment of own working capital, this source is formed in the process of distribution by the participants of the undistributed profit of the enterprise. At the same time, the direction of retained earnings for replenishment of own working capital is reflected in the debit of account 84 "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" in correspondence with account 83 "Additional capital".
9. Reserves for future expenses and payments
Reservation of forthcoming expenses according to the new chart of accounts is carried out on account 96 "Reserves of forthcoming expenses". The procedure for their accounting has not undergone significant changes.
In accordance with the Regulation on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of July 29, 1998 No. 34n (as amended on March 24, 2000), for the timely and uniform (normative) inclusion of forthcoming expenses in production costs or of treatment and the correct determination of the financial result of the reporting period, enterprises can create reserves to cover future costs and other purposes provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as regulations of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
The main list of such upcoming costs, which should be guided by the enterprise in the formation of its accounting policy, is given in the specified provision (paragraph 72). The balance of unused reserves that are carried over to the next year must be subject to mandatory inventory and adjustment. The procedure for calculating the amounts of reserves that are carried over to the next year is set out in the Guidelines for the inventory of property and financial obligations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of June 13, 1995 No. 49. on the:
forthcoming payment of vacations to employees (including social tax);
payment of annual remuneration for the length of service and remuneration based on the results of work for the year;
repair of fixed assets;
forthcoming costs for land reclamation, implementation of other environmental measures;
warranty repair and warranty service;
covering other foreseen costs and other purposes.
Estimated reserves accounts - 14 "Reserves for depreciation of material assets", 59 "Reserves for depreciation of investments in securities" and 63 "Reserves for doubtful debts" - in the 2000 chart of accounts act as regulatory contractual accounts and to the equity of the enterprise are only indirectly related.